Flutter Tips 15-21
April 25, 2020 • ☕️ 4 min read
#Day15 Flexible vs Expanded
Expanded() is nothing more than Flexible() with
Flexible (fit: FlexFit.tight) = Expanded()but, Flexible uses fit :FlexFit.loose by default.
FlexFit.tight = Wants to fit tight into parent taking as much space as possible.
FlexFit.loose = Wants to fit loose into parent taking as little space as possible for itself.
flex = The factor of space taken from parent. Mostly not fully used if flex: FlexFit.loose used i.e. Flexible.
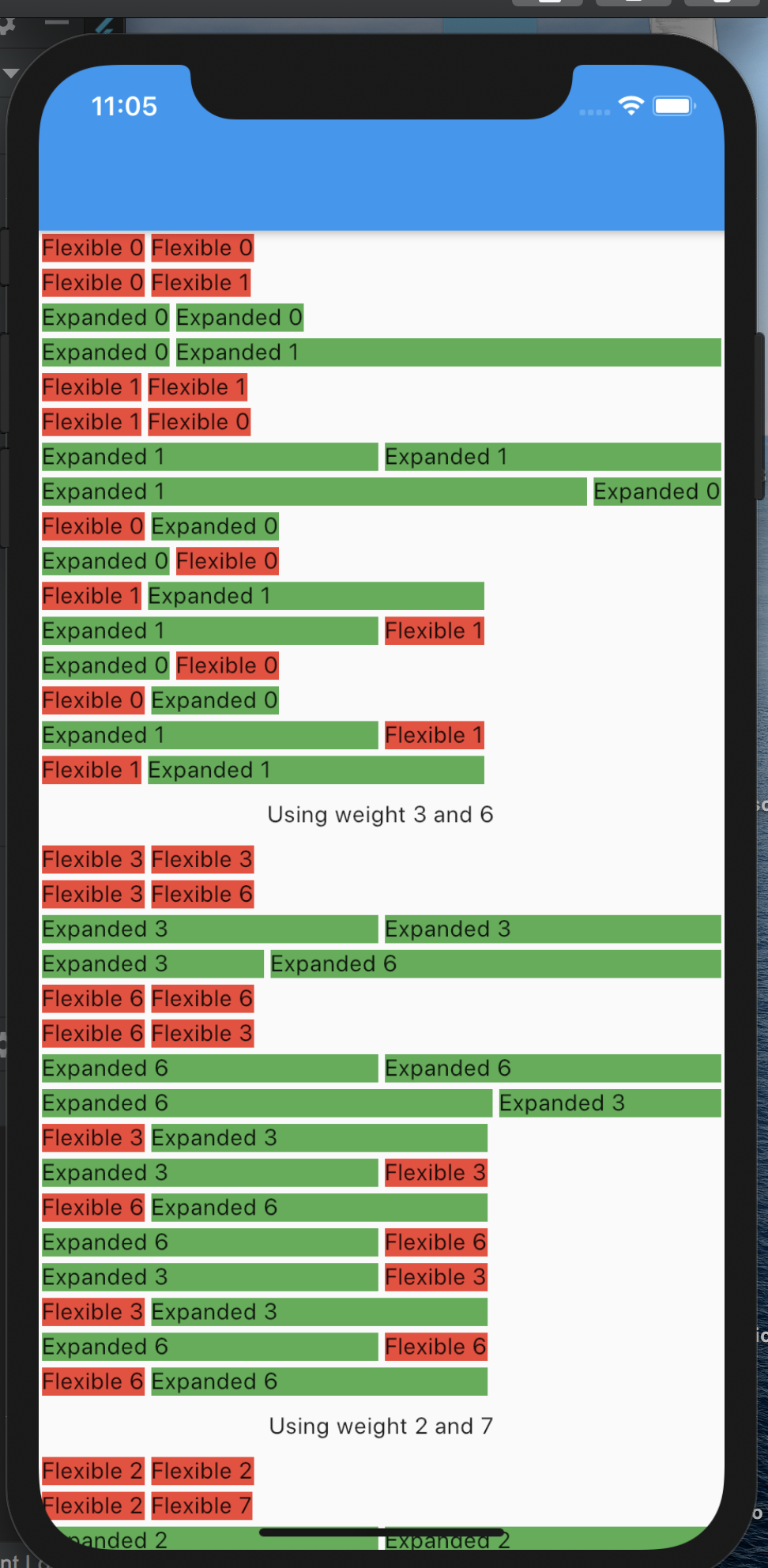
If you fully read the following image, you will fully understand the difference between Flexible and Expanded

#Day16 Bulk declaration
If you have been declaring each member separately all the time, you can declare members of same types at once.
I wouldn’t declare age and shoeSize at once because they are not related.
With great power comes great responsibility, Use this wisely.

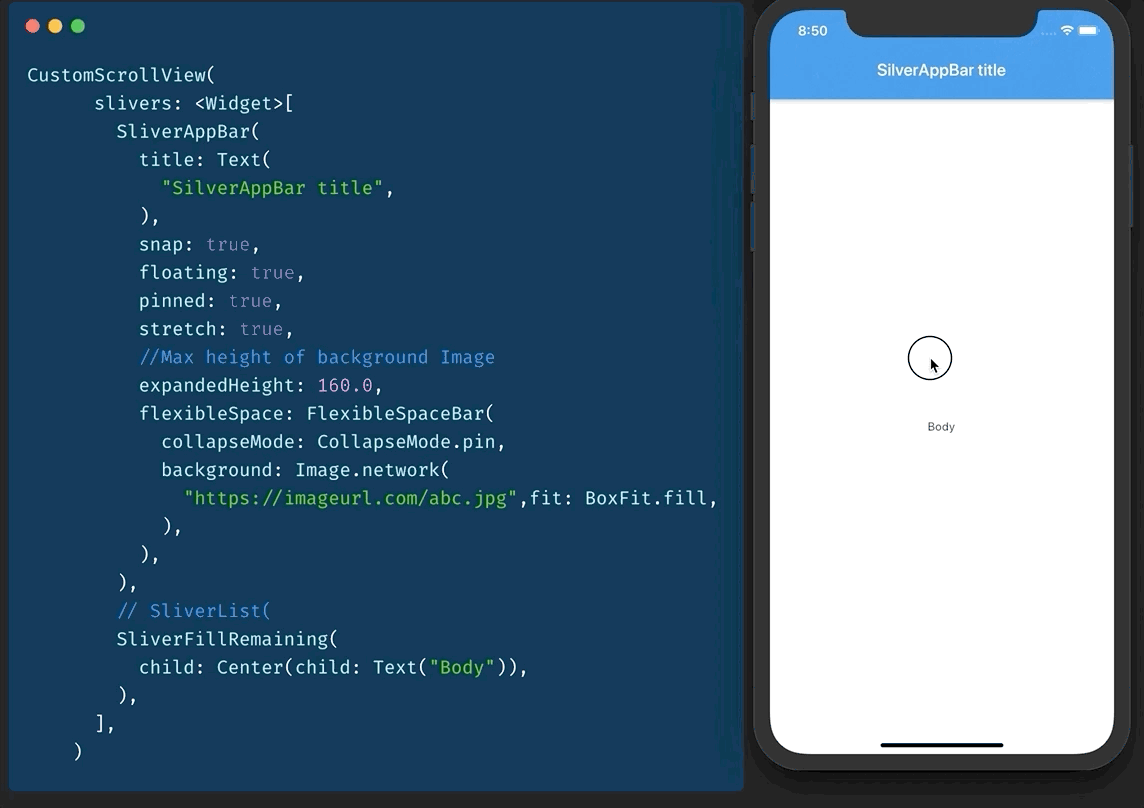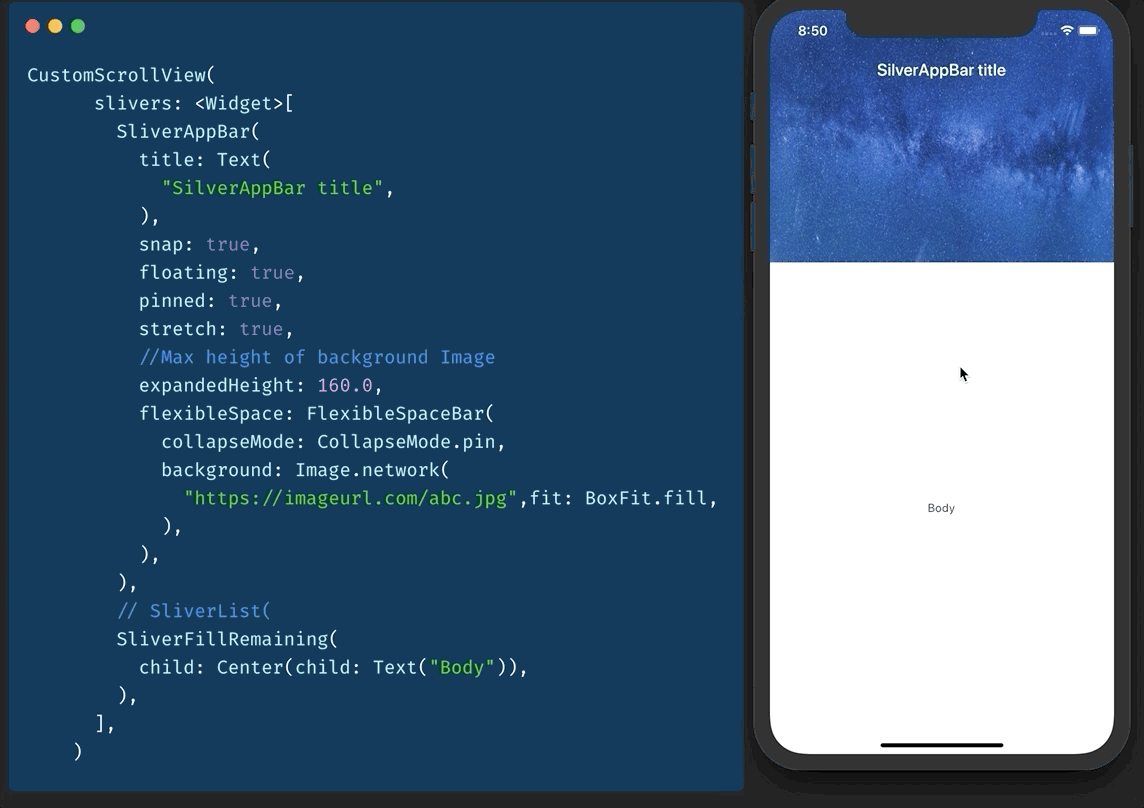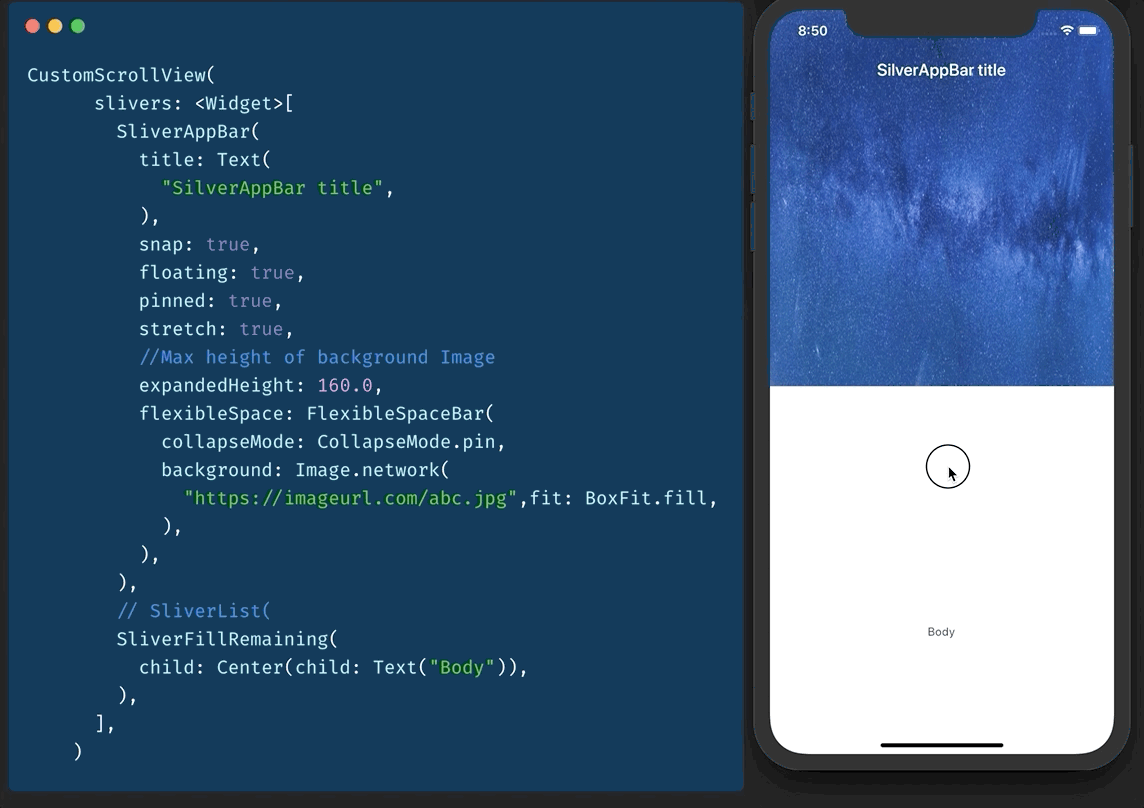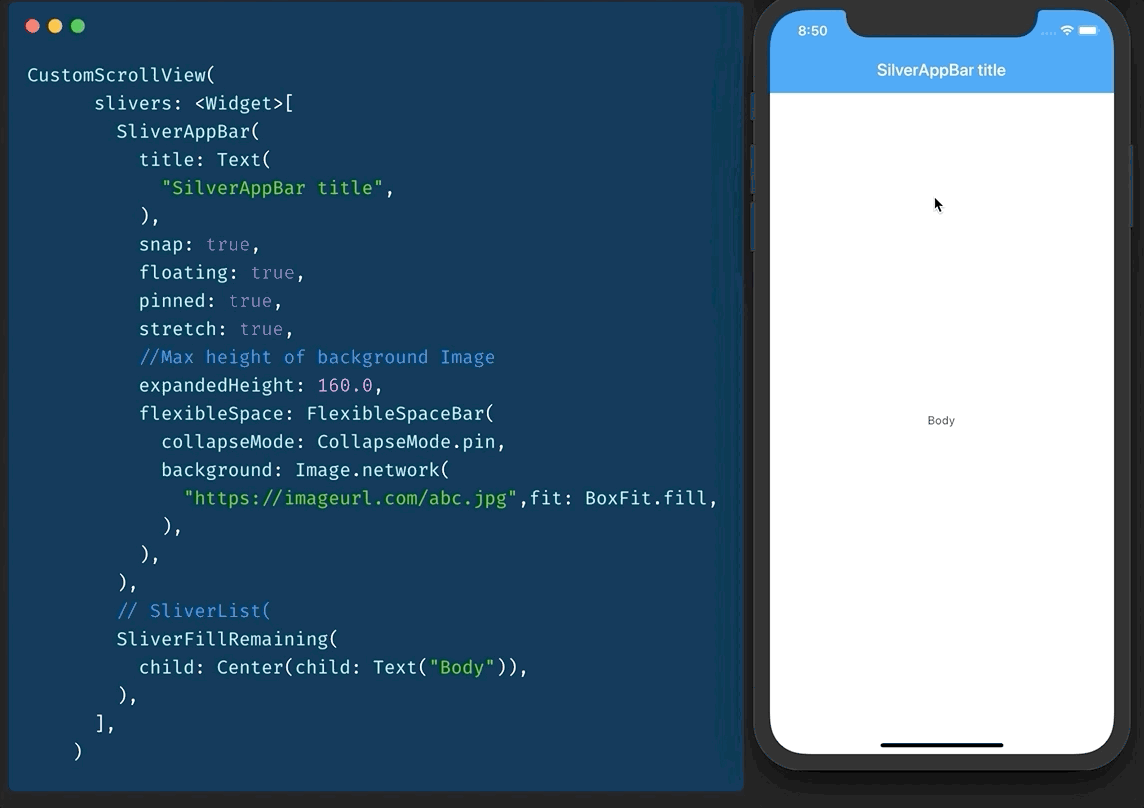
#Day17 SliverAppBar / Collapsable AppBar / ParallaxHeader
Remember CollapsableAppBar (android) / ParallaxHeader (ios)? We have SliverAppBar in Flutter to do exactly that.
To use it, you will have to have a CustomScrollView as parent.
then you add two slivers of it.
- SliverAppBar
- SliverFillRemaining
You can play with values of snap, floating, pinned etc to get desired effect
see various types of SliverAppBars here
#Day18 What the Key
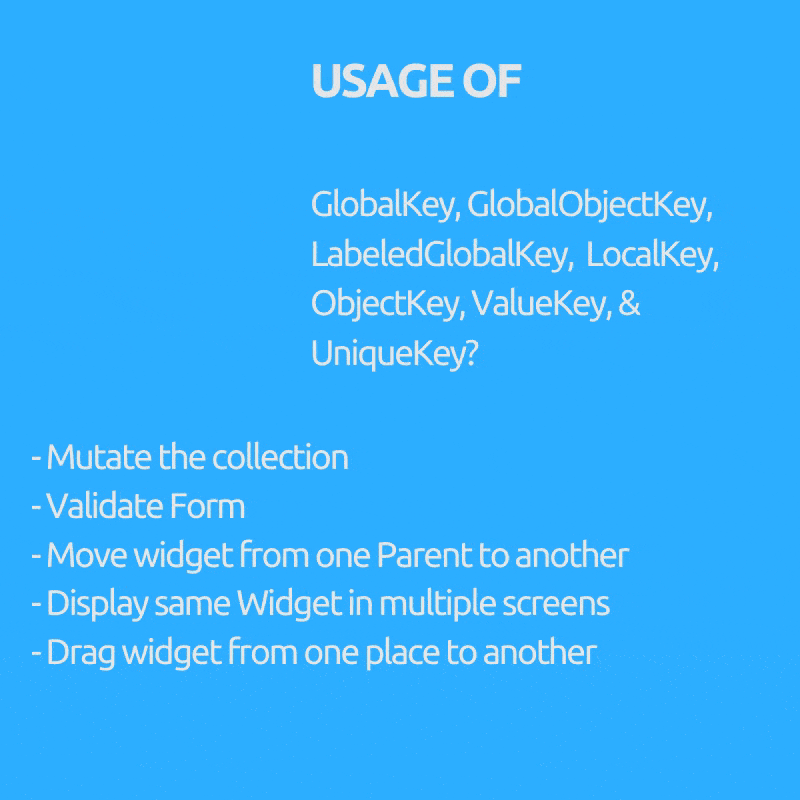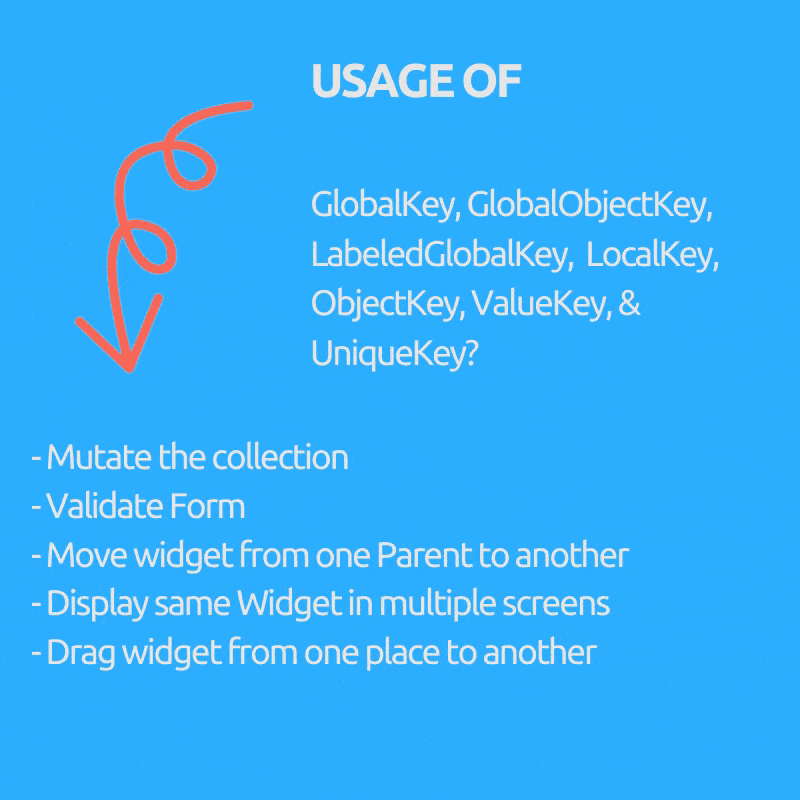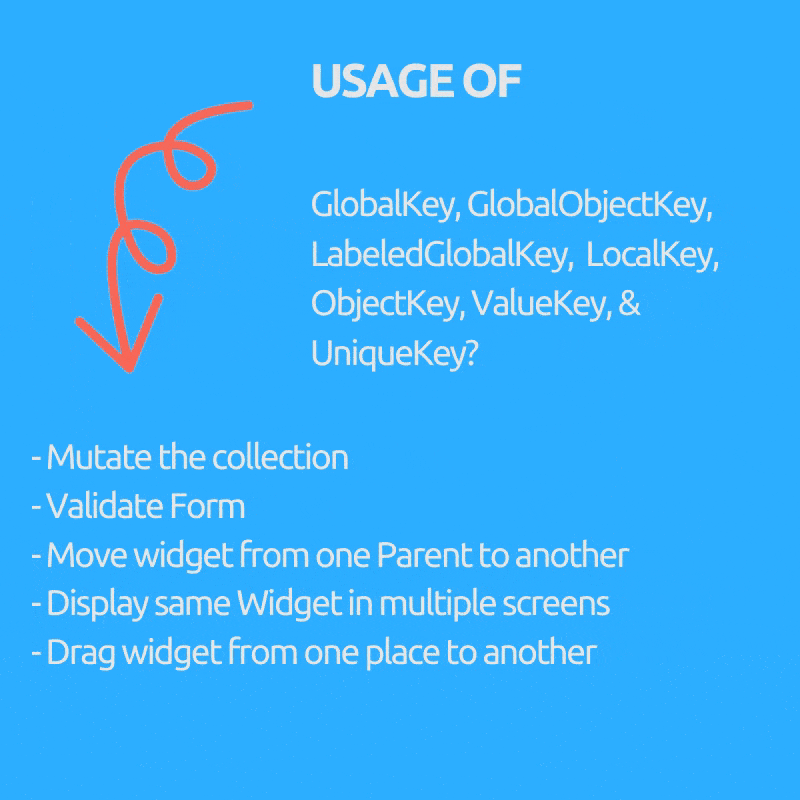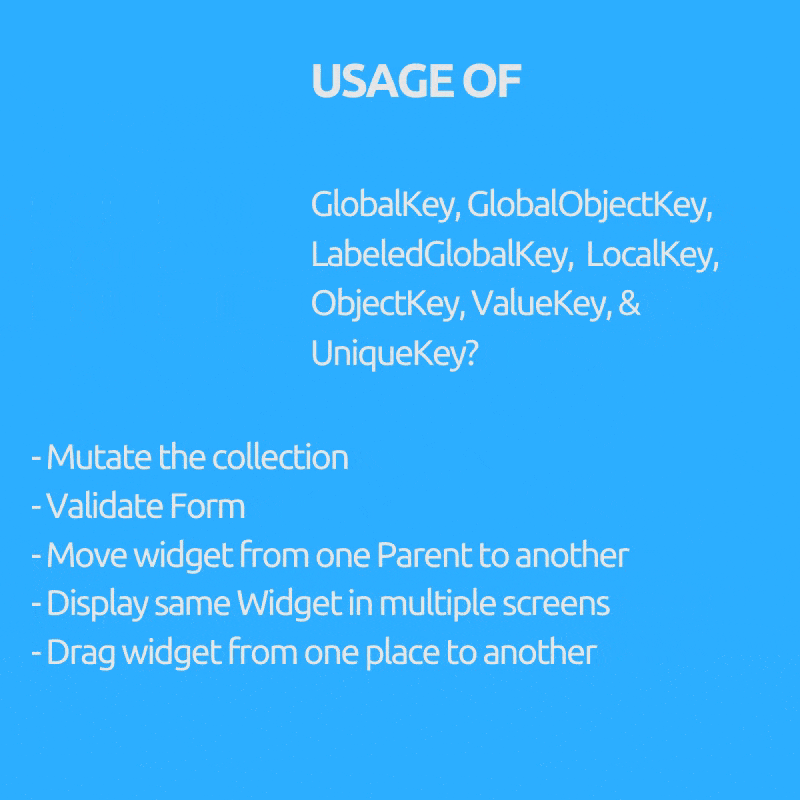
Ever wondered why we need GlobalKey(children : GlobalObjectKey, LabeledGlobalKey), LocalKey(children: ObjectKey, ValueKey & UniqueKey) right?
They are used to access or restore state In a statefulWidget (Mostly we don’t need them at all if our widget tree is all Stateless Widgets).
Purpose (Key to use inside bracket)
- Mutate the collection i.e. remove / add / reorder item to list in stateful widget like draggable todo list where checked items get removed (ObjectKey, ValueKey & UniqueKey)
- Move widget from one Parent to another preserving it’s state. (GlobalKey)
- Display same Widget in multiple screens and holding its state.(GlobalKey)
- Validate Form.(GlobalKey)
- You can to give a key without using any data. (UniqueKey)
- If you can use certain field of data like UUID of users as unique Key. (ValueKey)
- If you do not have any unique field to use as key but object itself is unique. (ObjectKey)
- If you have multiple Forms or Multiple Widgets of same type that need GlobalKey. (GlobalObjectKey, LabeledGlobalKey whichever is appropriate , similar logic to ValueKey and ObjectKey)
#Day19 Amazing Library Time.dart
If you are tired to long and verbose DateTime and Duration calculation Time.dart comes to your rescue.
//Before
var 3dayLater = DateTime.now().add(Duration(days: 3)).day;
//After
var 3dayLater = 3.days.fromNow.day;
//Before
var duration = Duration(minutes: 10) +Duration(seconds: 15) -
Duration(minutes: 3) +Duration(hours: 2);
//After
var duration = 10.minutes + 15.seconds - 3.minutes + 2.hours;
//Before
await Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 2))
//After
await 2.seconds.delay#Day20 Testing errors
You can simply test if two values are equal in dart with expect(actual, expected)
But if you want to test errors use the function closure that throws error as actual and check with throwsA<ErrorType> as expected.
void main() {
group("Exception/Error testing", () {
test("test method that throws errors", () {
expect(_testError(fails: false), false);
expect(() => _testError(fails: true), throwsA(isA<FooError>()));
});
});
}
bool _testError({bool fails}) {
if(fails)throw FooError();
return fails;
}
class FooError extends Error {}#Day21 Concisely add collection into collection with Spread(...) operator
We normally use addAll() on collection to add one collection to another.
But From dart 2.3 and above, we can use Spread Operator (...) to add collection inside collection.
